Conversation Context
Introduction
Conversation Context enables your Assistant Agent to gather and store variables from conversations with users. These Conversation Variables can be referenced and used later in the agent's execution, allowing the agent to personalize responses, make decisions, or trigger actions based on previously collected information. If you need to collect contact emails, ratings, feedback on products, or other structured data, the agent will guide the conversation to obtain and store this information as Conversation Variables.
How to Use
In this example, we will use an existing agent to create a new Conversation Context and configure how Conversation Variables will be collected and stored during the conversation for later use in the agent's execution. For guidance on creating an Assistant Agent, refer to this guide.
Create a Conversation Context
-
Navigate to the Conversation Context card.
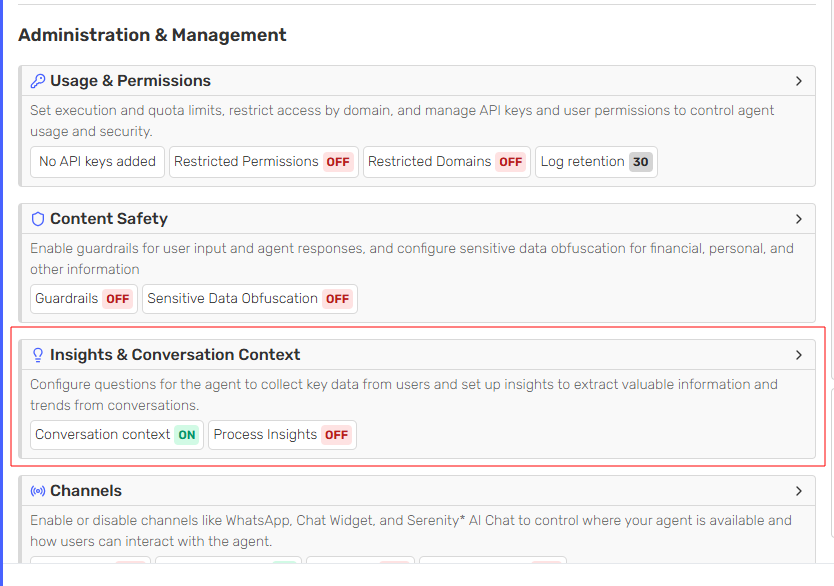
-
Click on the "Add Conversation Variable" button.
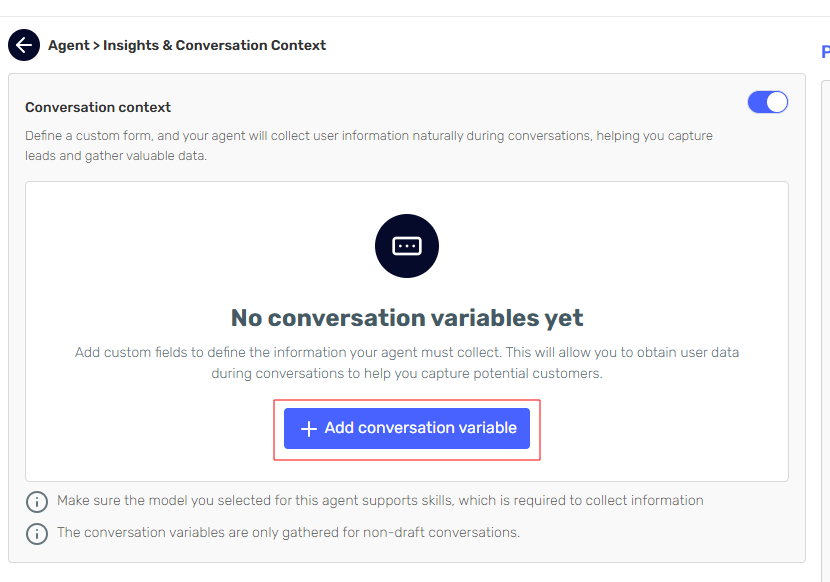
-
Select the data type you wish to collect. Different data types provide additional context for the agent to ensure the correct information is gathered and stored as Conversation Variables for later use.
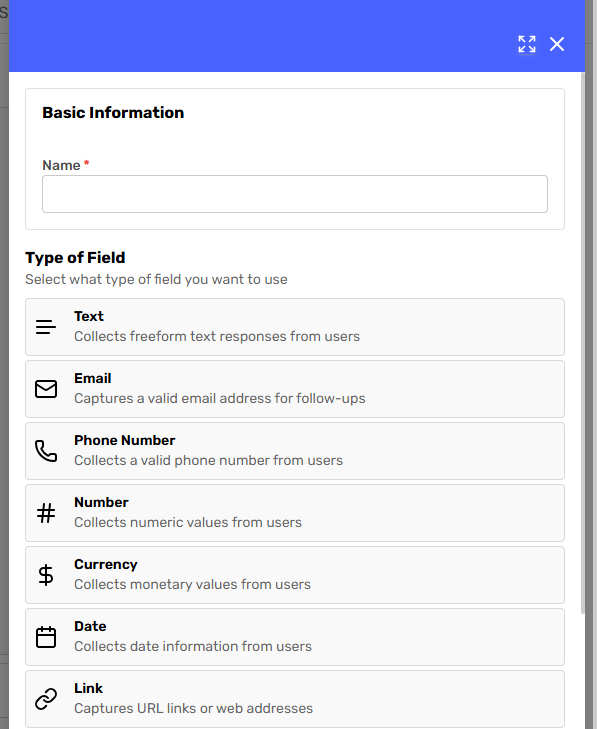
-
Define how the agent should complete the variable. Include the name and provide any additional instructions for the agent to collect, validate, and store the Conversation Variable for later use in the conversation or agent logic.
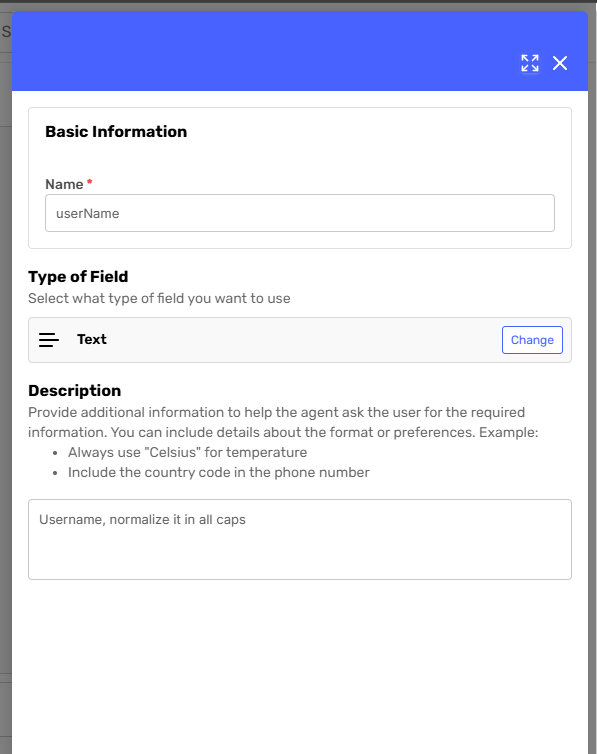
-
Specify in your agent's behaviour, additional instructions on how to obtain or guide the conversation flow. You can also use liquid templating functionality to create custom logic inside your prompt based on what the agent stores in the variable.
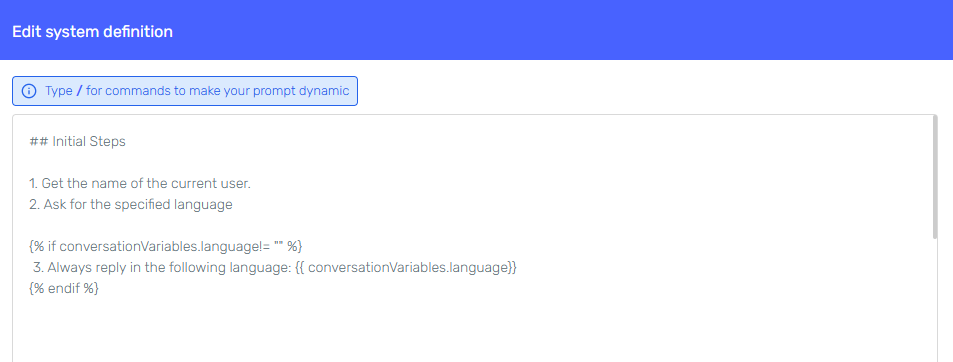
-
Test the agent using the preview chat. Evaluate its performance and how it steers the conversation. Adjust your prompts, Conversation Variable descriptions, and instructions based on your expected behaviour. Once you are satisfied with the results, publish your agent and begin collecting and using Conversation Variables in your agent's logic.
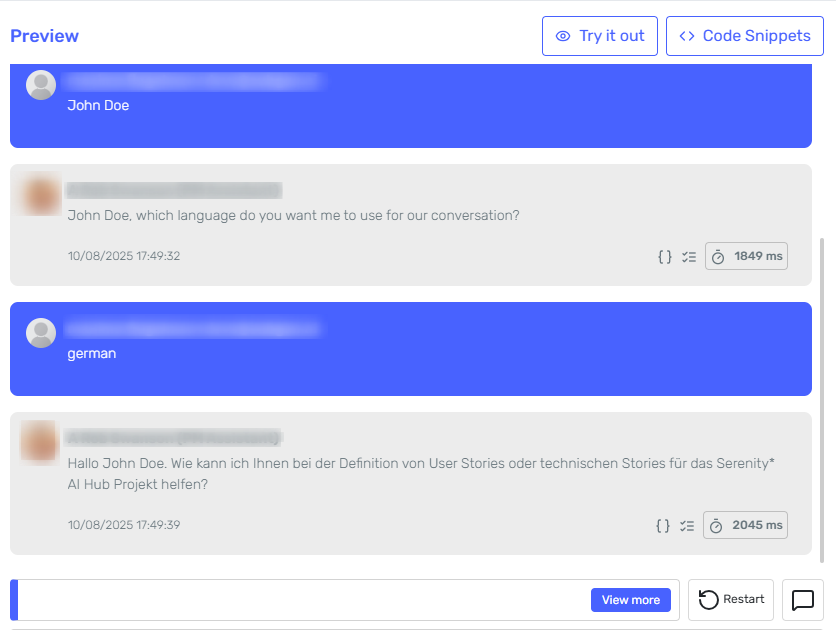
Note: Conversation Context data retrieved in draft versions of the agent is not included in the final data collection, nor will it be available for use in agent execution until published.
Access Conversation Context Data
Conversation Context can be used as a data recolection tool. Once your agent is published and collecting Conversation Context data, you can access it from the agent card by clicking the "Conversation Context" button. On this page, you can view all the Conversation Context data collected by the agent, export it to an Excel file, and see how Conversation Variables are being used in agent execution.

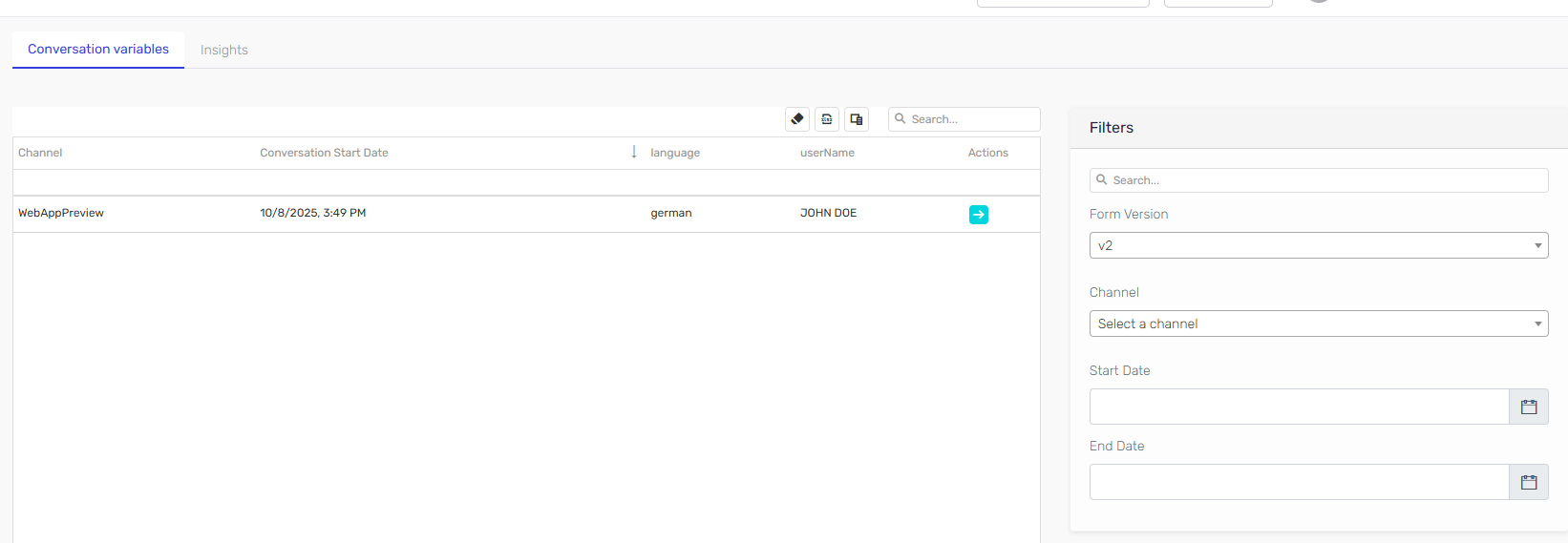
Conversation Contexts are versioned; each change to the Conversation Context definition creates a new version linked to the version of the agent. If changes are made to the agent but not to the Conversation Context definition, the Conversation Context version remains the same when saving the changes. From the Conversation Context grid, you can filter collected data by version. By default, the Conversation Context corresponding to the published agent is shown first.
Tips
- Clear Instructions and Conversation Variable Descriptions: Ensure consistency between agent behaviour and Conversation Variable descriptions to promote predictable outcomes and effective use of stored variables.
- Data Validation: Specify any validation needed for the data, such as ensuring a valid email address is provided or that phone numbers include the country code.
- Model Selection: Conversation Context behavior may vary between different LLM models and tool usage support. Choose models that demonstrate strong support or understanding of the required skills.
Example Use Case
For a practical example of how Conversation Context can be used in a real-world scenario, see our blog post on Identity Verification in Conversational Agents - Context & Flow Control. This article demonstrates implementing an identity verification flow in a customer support agent for online order management, showcasing how conversation variables control multi-step validation and dynamic prompting.