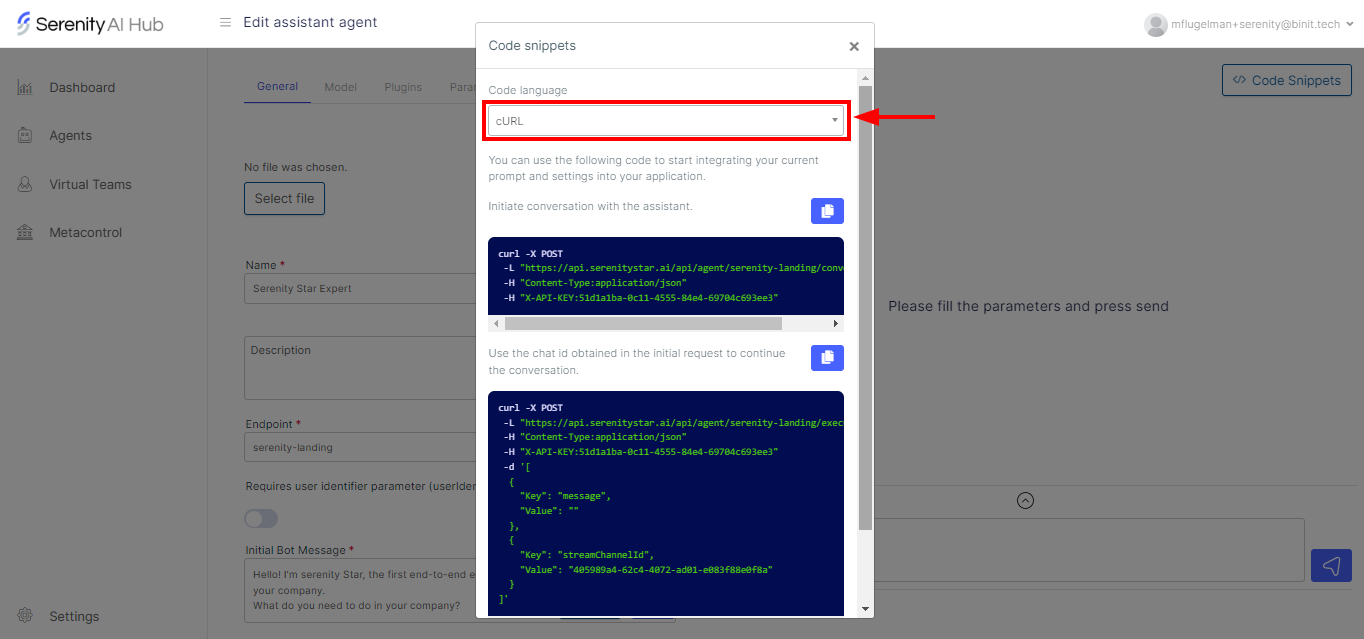
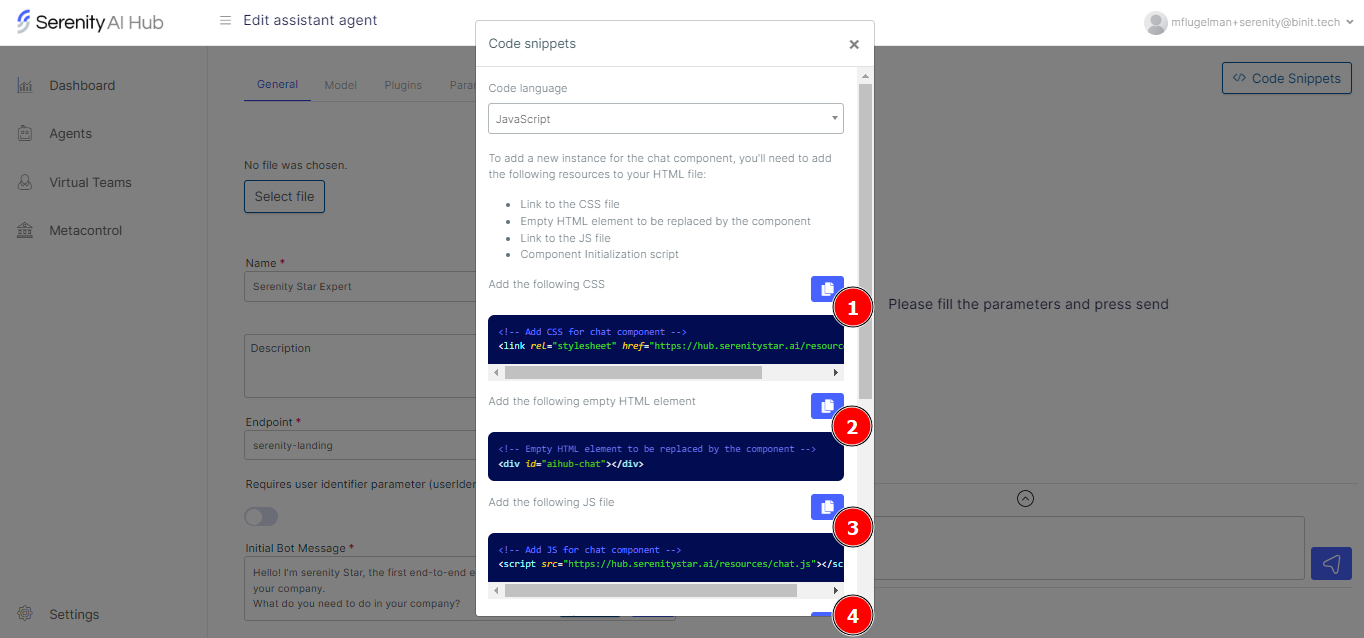
Serenity* Agents can execute HTTP requests via the HttpRequest Skill. This skill allows us to describe the endpoint we want to execute, including the method, headers, authentication, and body.
This article will explore how to use this skill to execute POST requests. We'll see how to configure this skill to provide an AI-generated body for the request and, most importantly, ensure the agent knows how to build a valid body and when to use each skill.
We'll iterate from a simple starter agent to a more robust one, testing and improving it along the way.
About the example
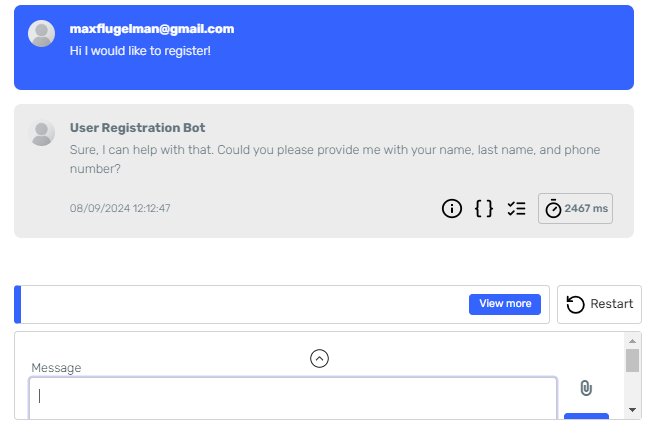
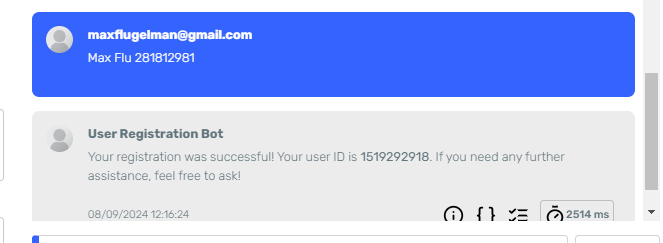
We'll create an agent whose goal will be to help us schedule meetings and events based on a prompt.
For this example, I created a mock API with two endpoints:
POST /meeting/schedule to schedule a meetingPOST /event/schedule to schedule an event (used for reminders or something that doesn't require attendees)
Both endpoints are intentionally similar, so we can demonstrate how to instruct the agent to use the right skill for each case.
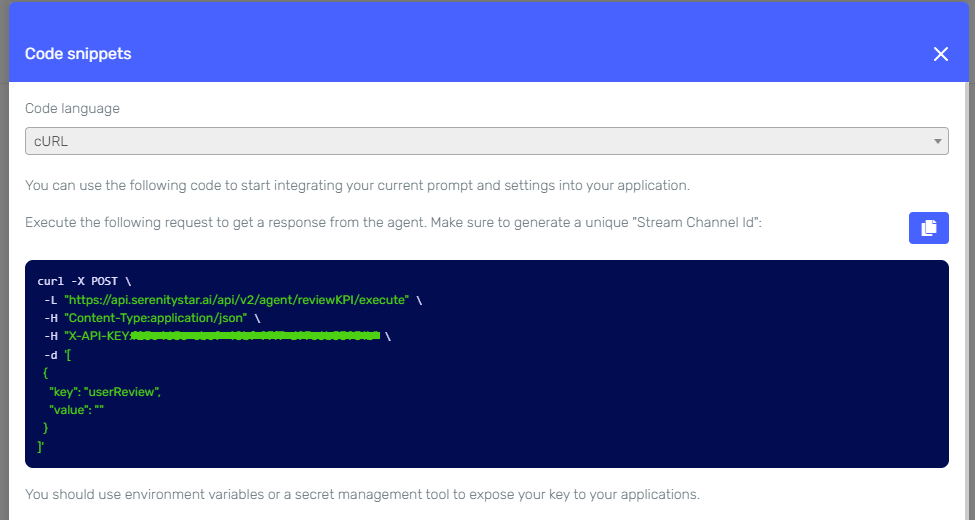
We'll give our agent access to these endpoints via the HttpRequest Skill.
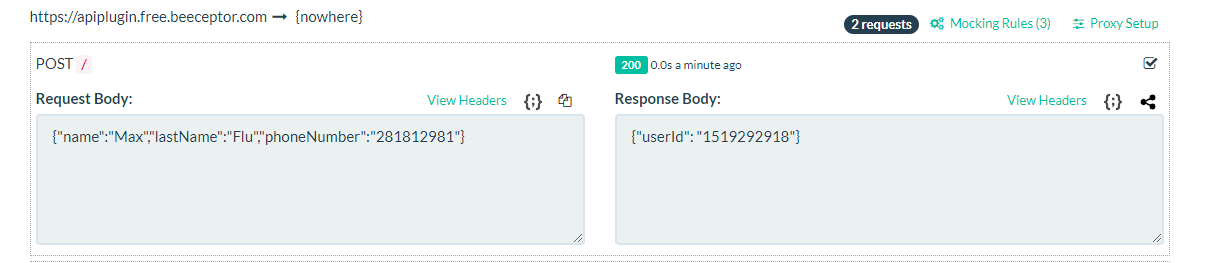
For example, if the agent receives a prompt like "Schedule a meeting for the product demo on September 22nd at 3 pm. It should take 45 minutes," it should execute the following request:
curl -X POST "https://<my-mock-api>/meeting/schedule" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"datetime": "2025-09-22T15:00:00",
"duration": 0.75,
"subject": "Product demo",
"attendees": [],
"location": null,
"description": null
}'
Setting up the Agent
For this example, we will create an Activity agent. It will receive a prompt that will be used to decide which skill to use, if any.
General Tab
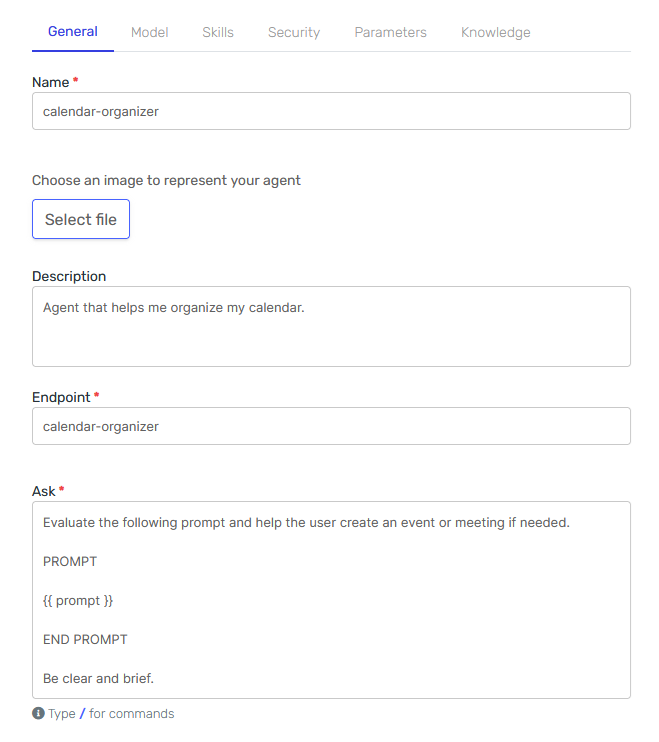
The main thing to notice here is the "Ask" field. That's the instruction the agent will receive. As you can see, it includes an input parameter called prompt.
We'll keep it simple for now.
Model Tab
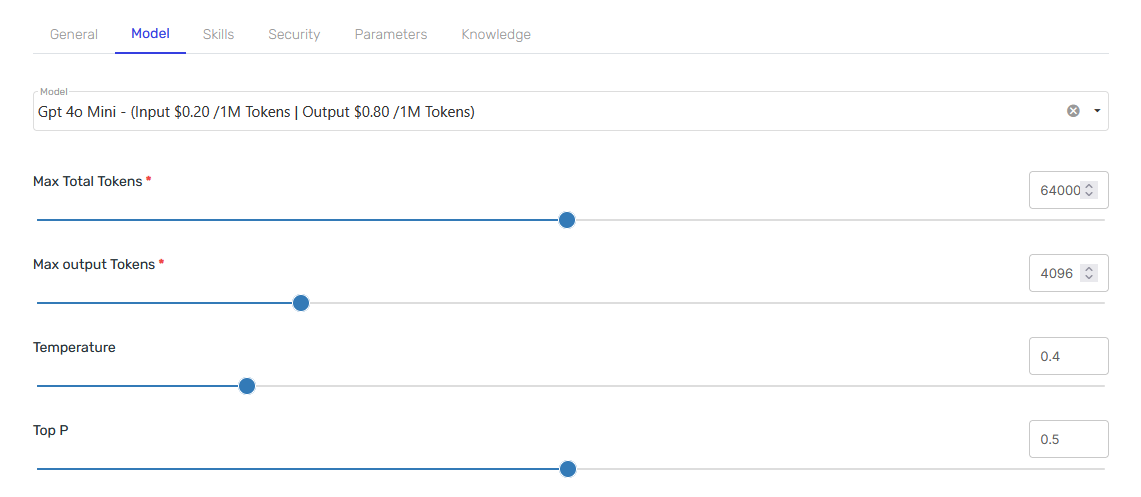
In this tab, select OpenAI's GPT 4o Mini and leave everything else as default.
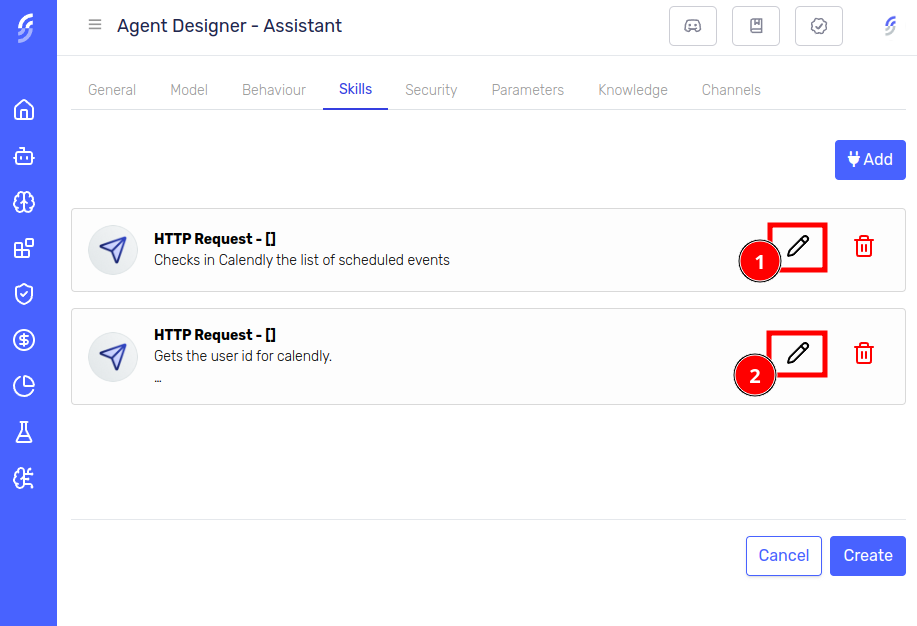
Skills Tab
Time to add our two HTTP Request Skills.
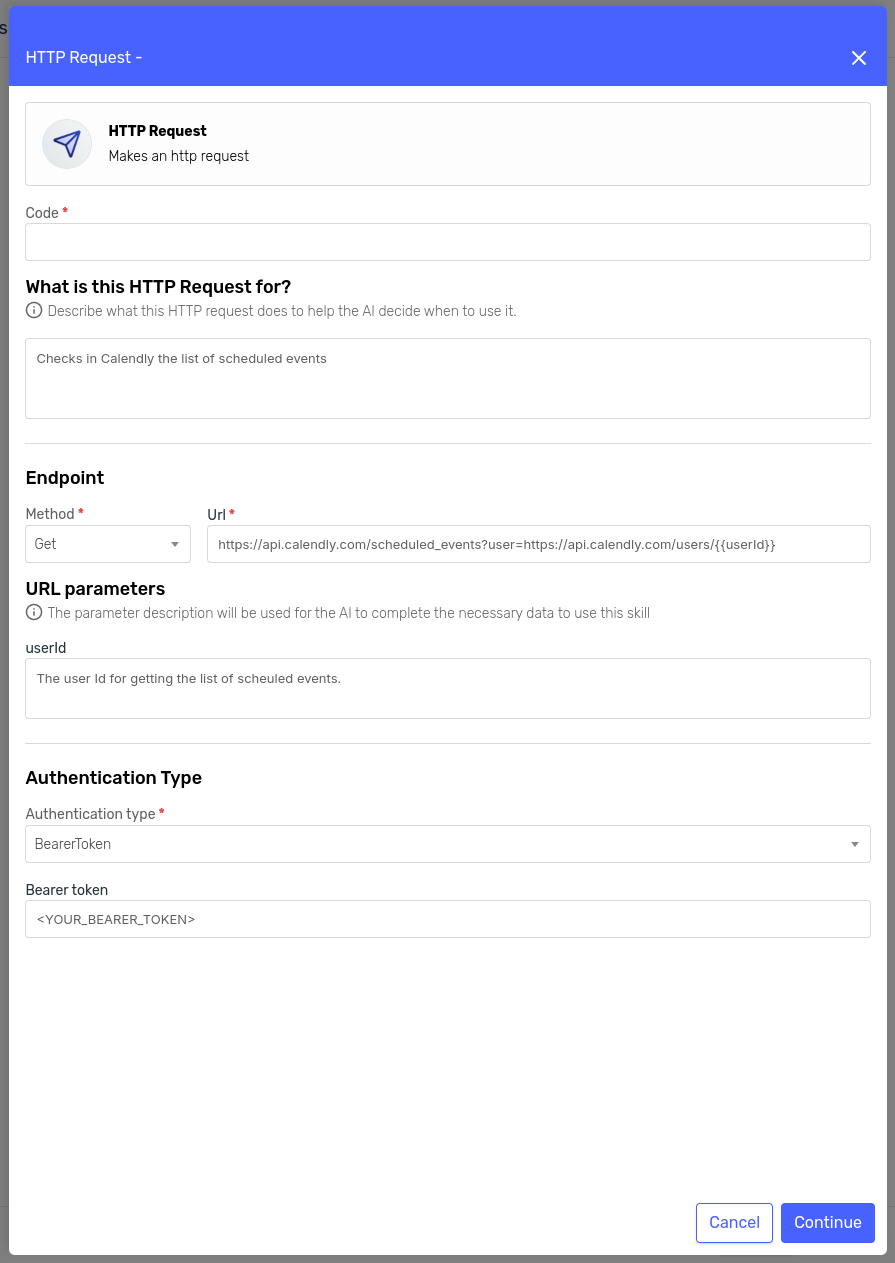
Meeting Skill
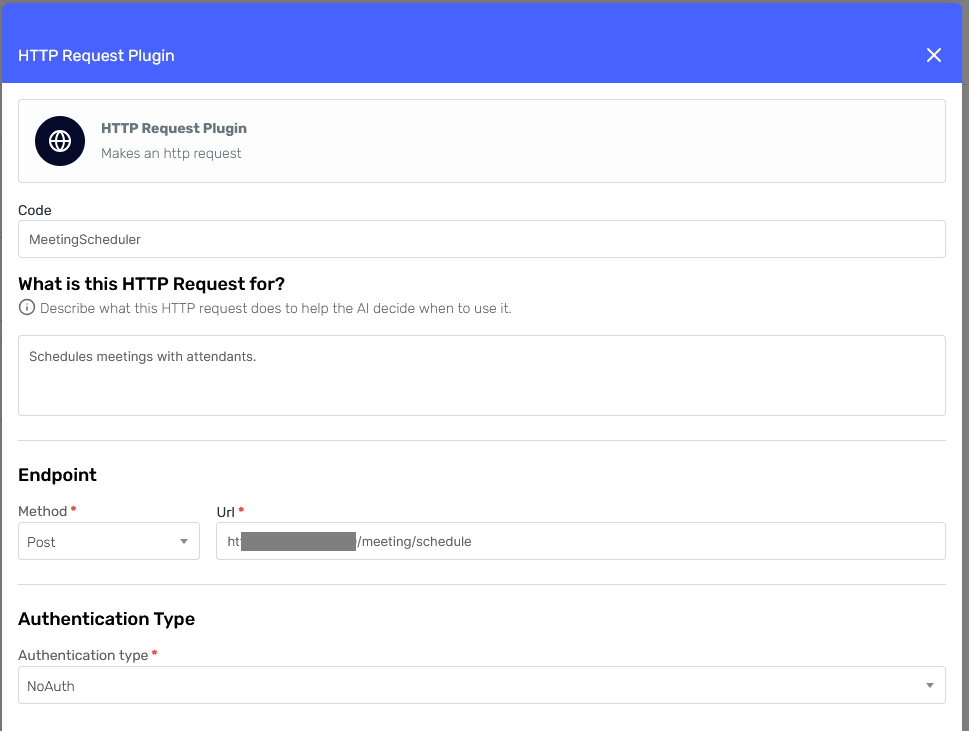
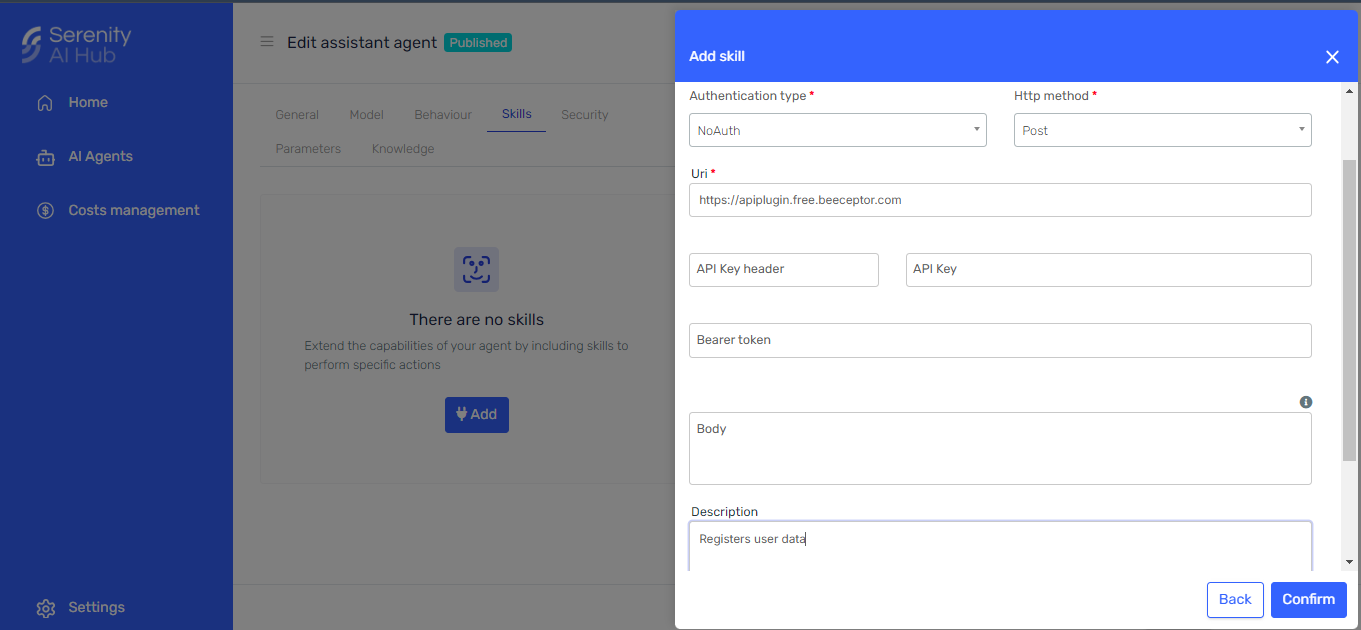
The first section of the form asks us for the following information:
- Code: This should be a unique code to identify this particular skill. It will also help us identify the skill in the agent's response and logs.
- Description: Describe what the skill does, when to use it, any important notes or limitations we want the agent to consider, etc.
These two fields are extremely important for the agent to determine when and how to use each skill. In this first iteration, we'll keep them brief and simple so we can see the difference when we improve them later.
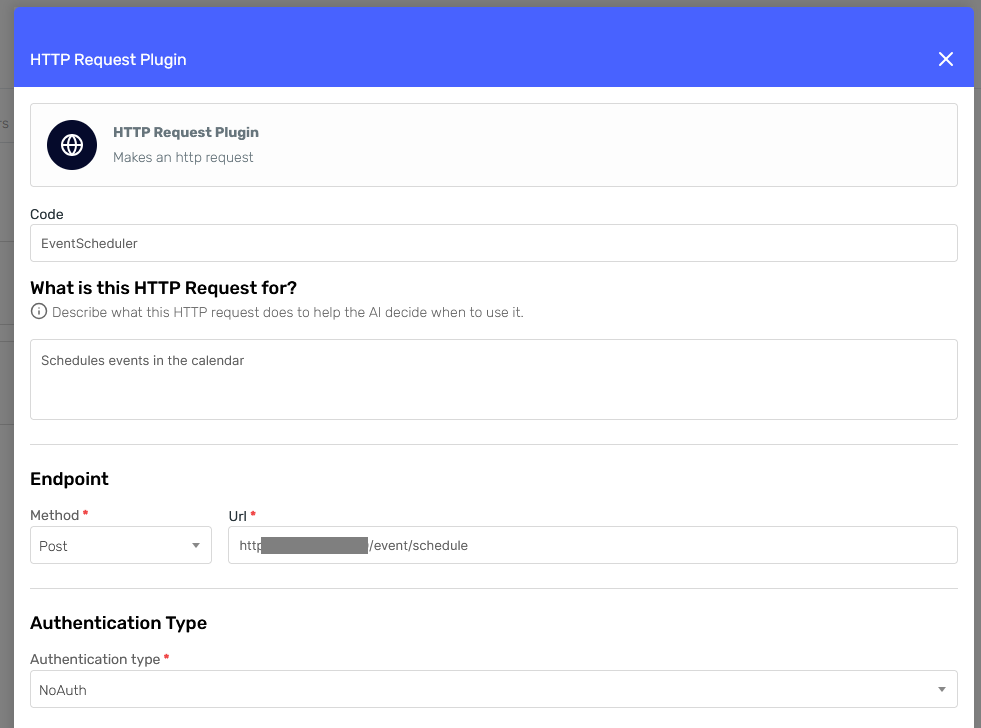
For the Authentication Type, I'll select "No Auth" since my mock API doesn't require authentication.
Then, fill the Method and Url fields with the appropriate values for the meeting endpoint and press "Continue."
In the next section, we'll be asked to configure the headers and body.
We don't need to provide any headers in this case, so we'll leave that section as is.
For the body, turn on the "Include request body" switch and select "AI-Generated Body." This will instruct the agent to generate the body considering the body description we provide, as well as the prompt and skill description.
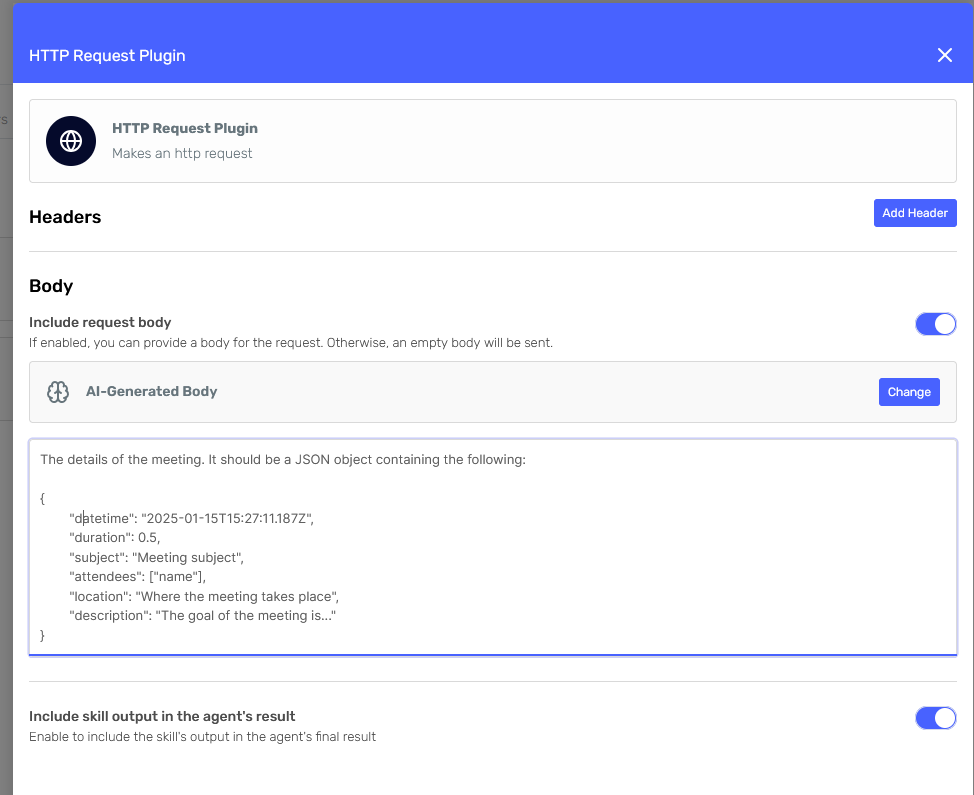
We'll simply provide a sample body with a brief description.
Finally, check the "Include skill output in the agent's result" switch at the bottom to include this skill's response in the agent's response. This will help us with our tests later.
And now, we can confirm this configuration and move on to the next skill.
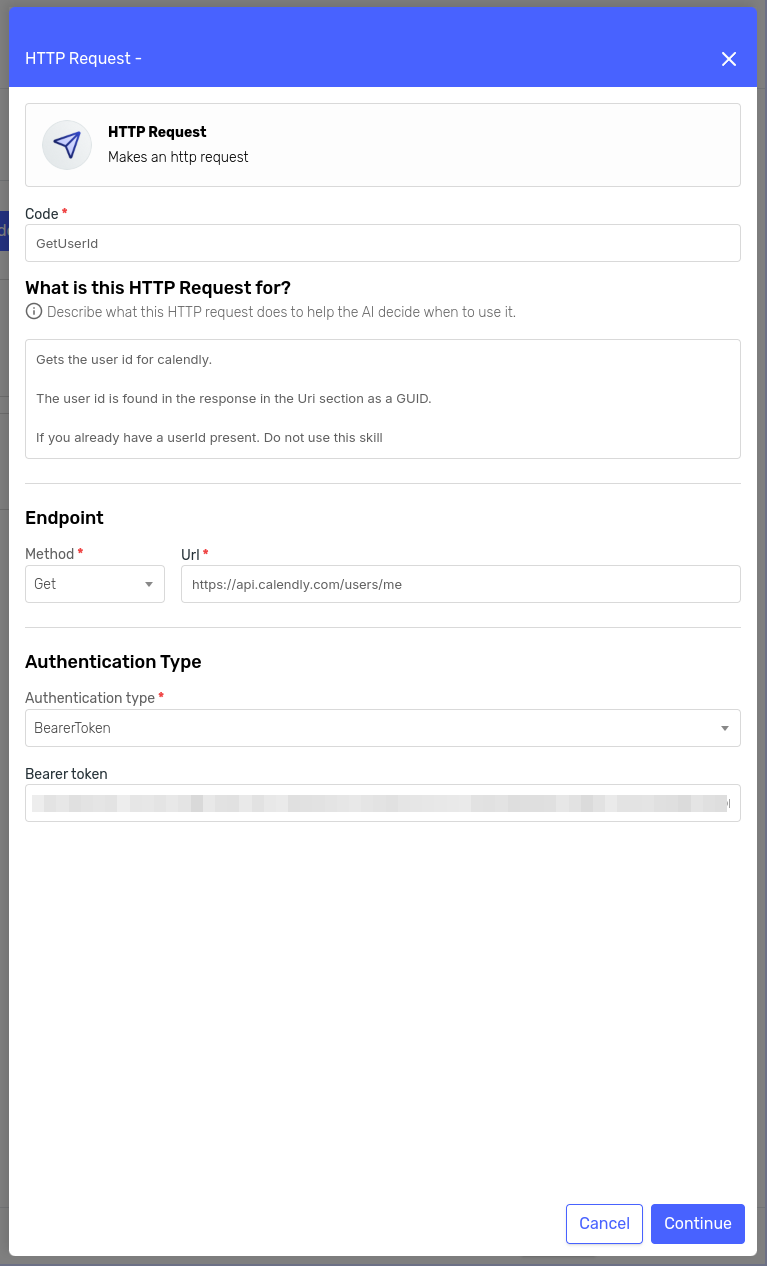
Event Skill
This configuration will be similar to the previous one, so I'll just show you the resulting forms:
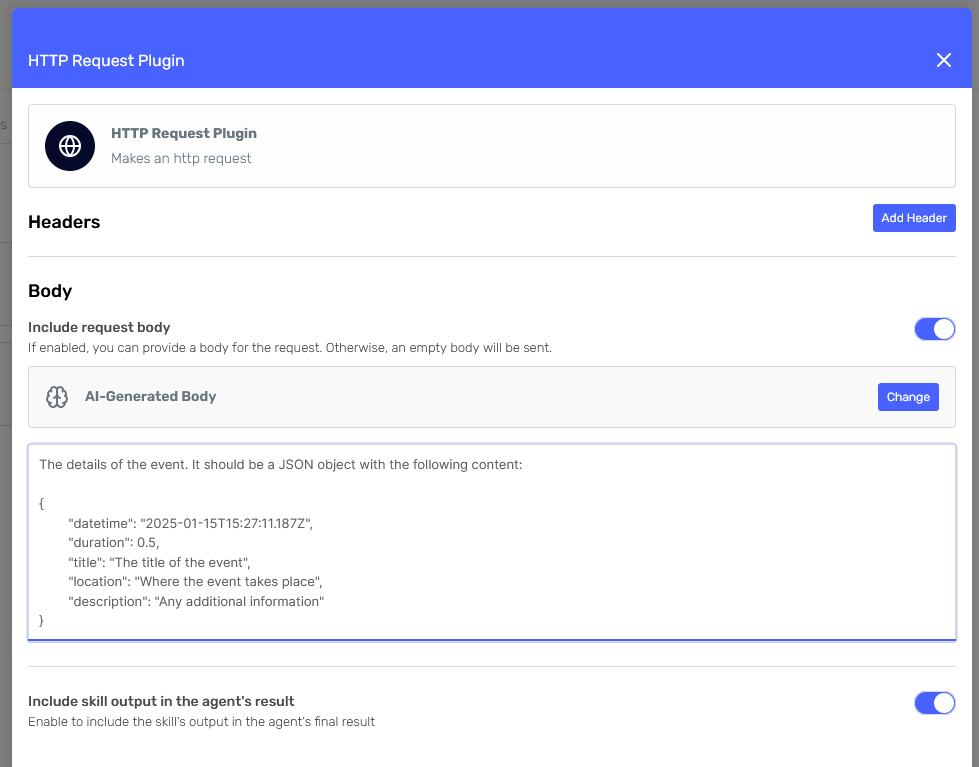
Now that the agent has skills, we can create it and begin testing.
Testing the first version of our agent
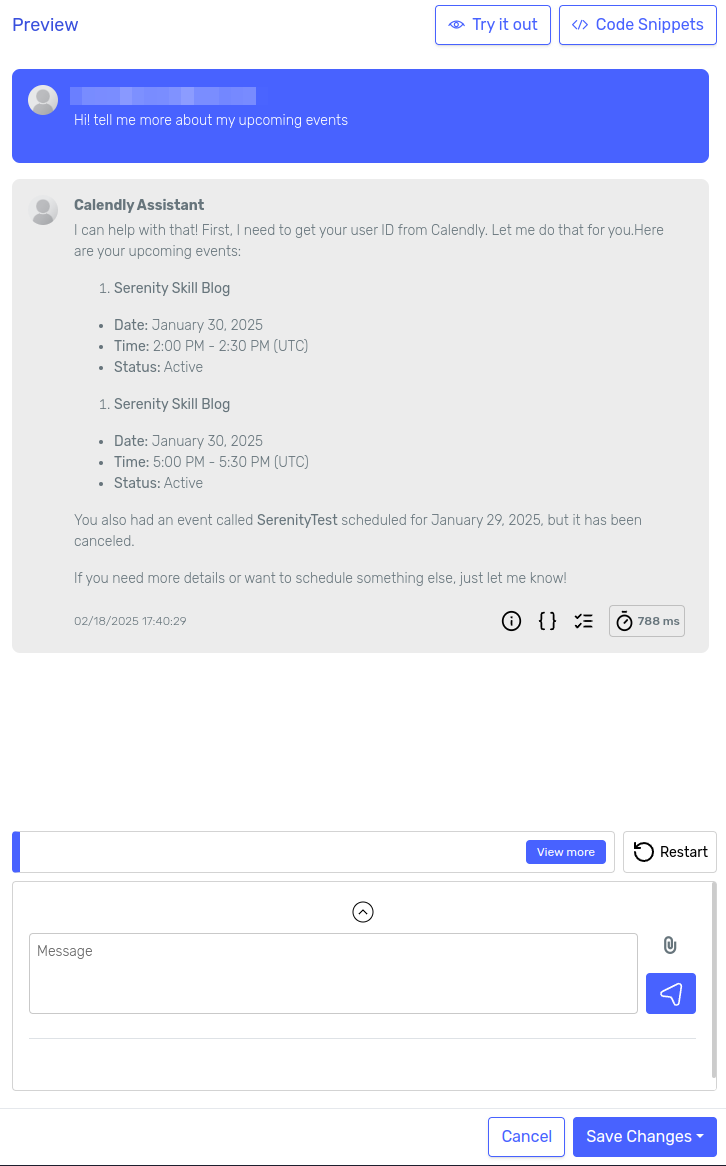
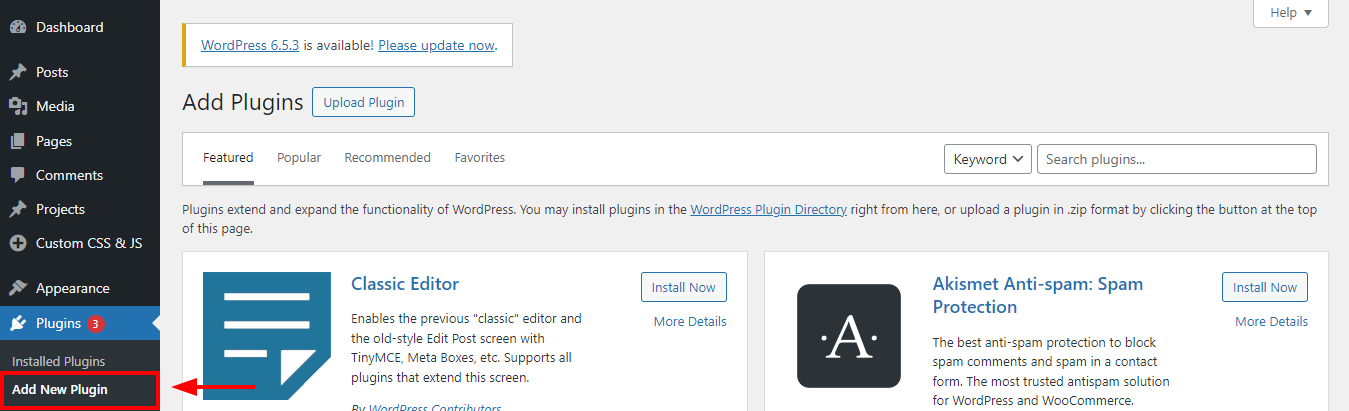
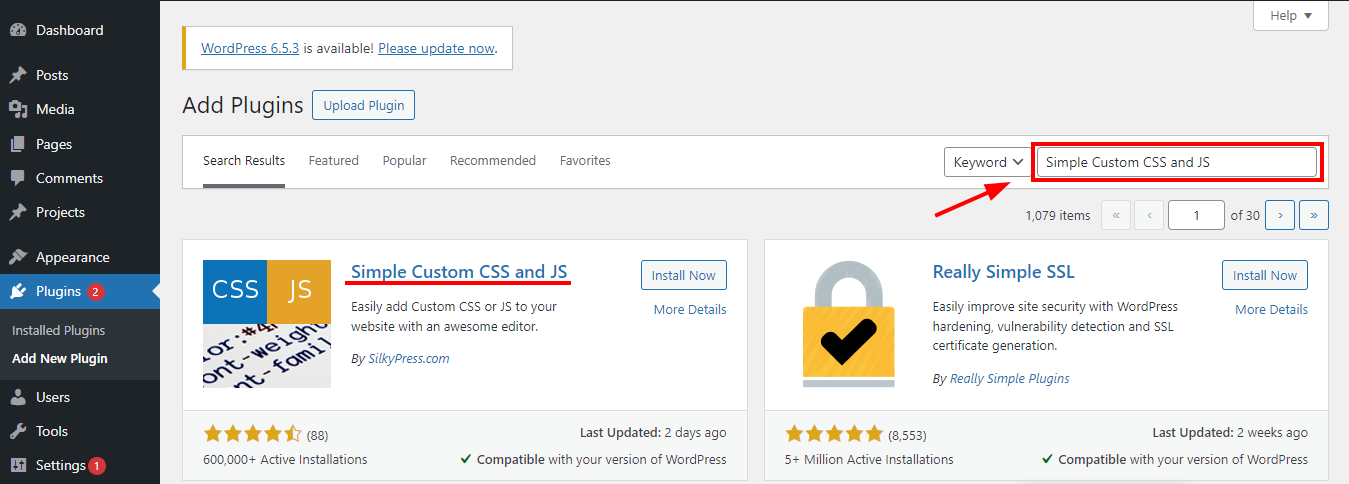
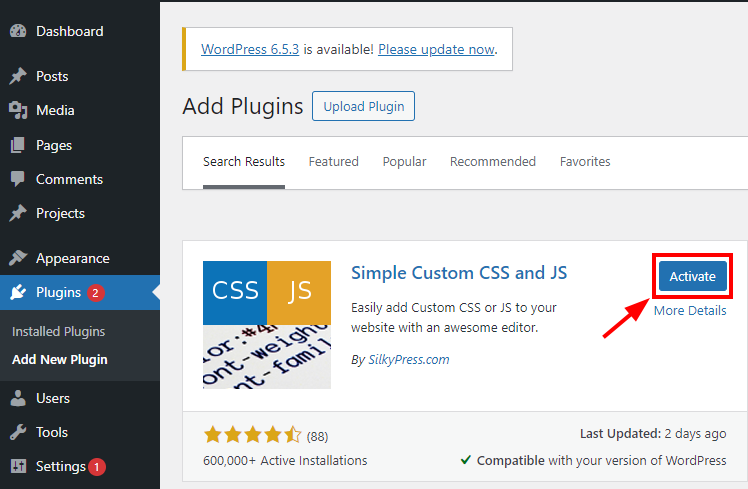
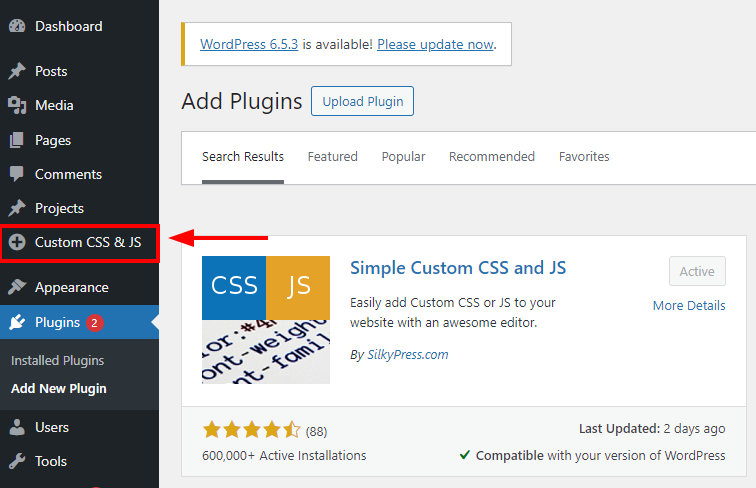
We can access our new agent from the "AI Agents" page. Click over the card to open the Agent Designer.
At the right side we have a "Preview" section where we can test our agent filling-in the prompt parameter with different values.
Let's try it.
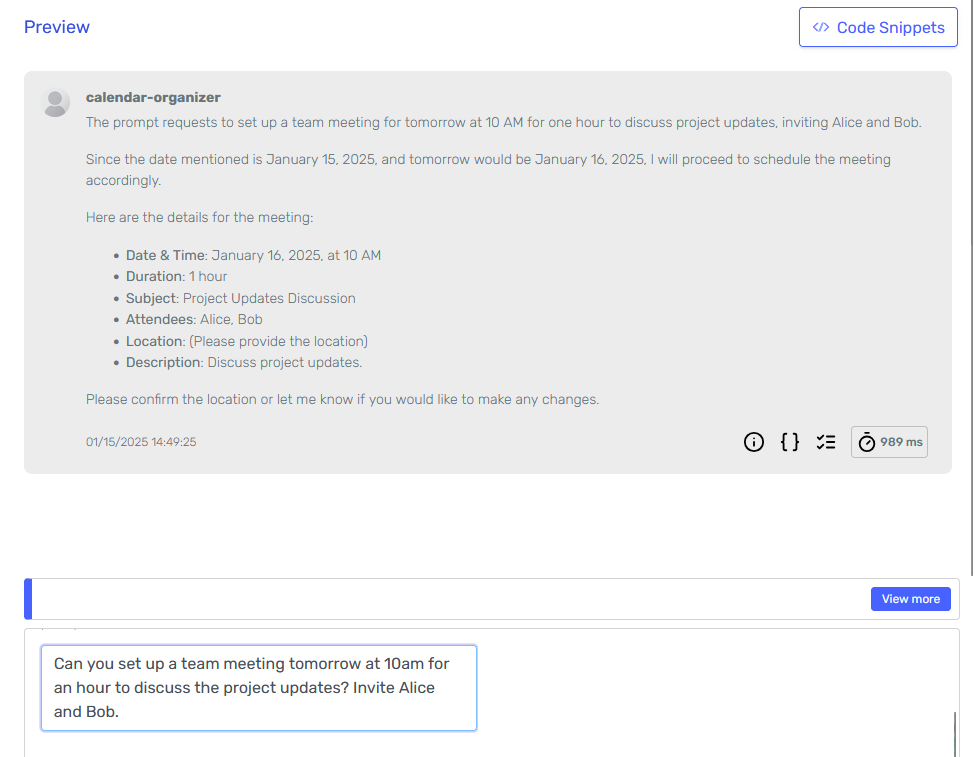
It seems like it understood the task, but taking a look at the logs I can see that it didn't invoke any of the skills and its asking for the location of the meeting. That's probably because I didn't specify which fields are optional when describing the body.
It also appears to be using the date I provided as an example (2025-01-15) as the current date.
Let's try adjusting the input prompt to see if we can get a better result:
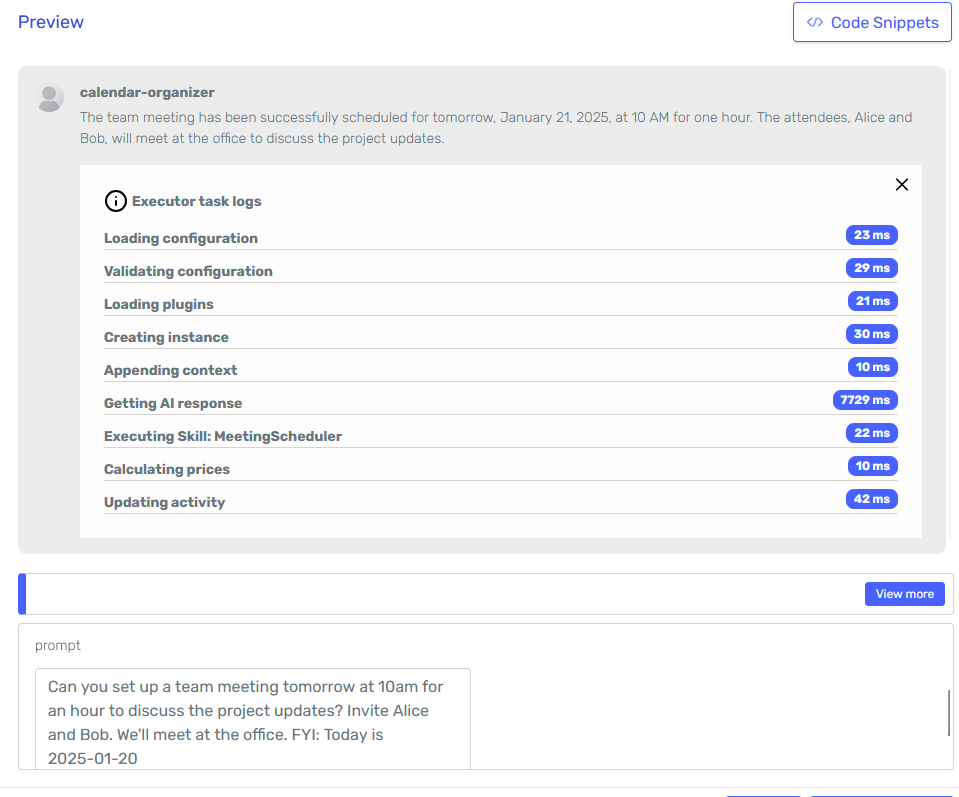
It seems the adjustments to the prompt did the trick, and now the agent is properly calling the MeetingScheduler skill.
Automated testing
One or two manual tests are not enough to ensure the agent is working as expected. Ideally, we should run a set of diverse tests that emulate real-world scenarios and evaluate the results to see where the agent is failing.
You can use Postman to run automated tests on your agent by providing a data file with many different test cases and using Postman's scripts to verify the results.
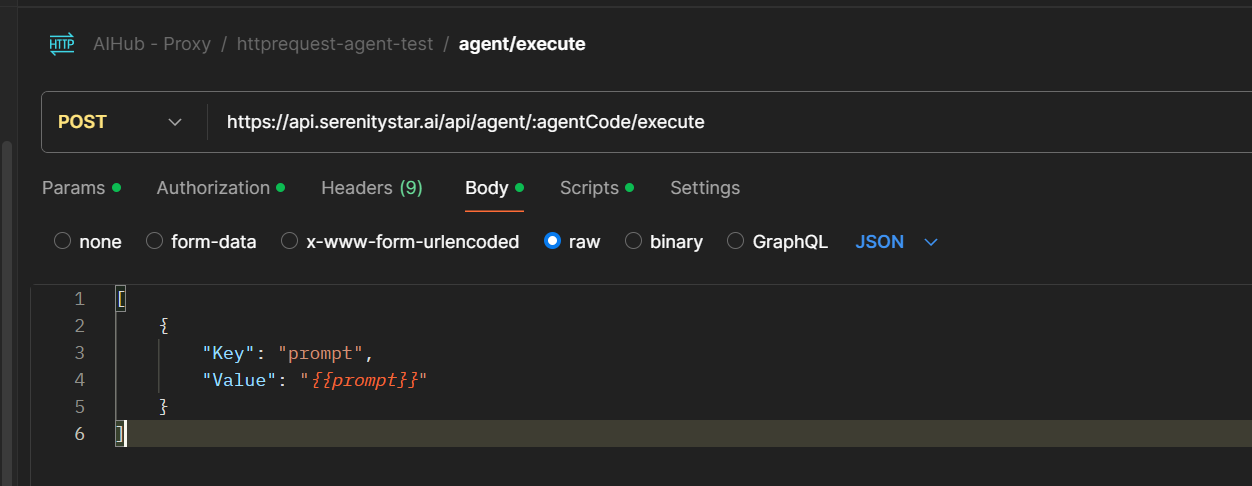
For example, in this case, I added a Postman endpoint where the body contains a variable for prompt, which will be replaced by the test data.
Here's a sample of my test data:
[
{
"prompt": "Arrange a meeting for the product demo on September 22nd at 3 pm. It should take 45 minutes.",
"type": "meeting"
},
{
"prompt": "Put the Leonid meteor shower on November 17th on my calendar. Starts at midnight.",
"type": "event"
},
{
"prompt": "Book a weekly sync with the design team next Thursday at 11 am for 30 minutes.",
"type": "meeting"
},
{
"prompt": "Add the company picnic to my calendar for August 25th. It starts at 10 am and lasts all day.",
"type": "event"
}
]
I also added a test script to verify the agent's response. This script checks if the agent used the right skill by comparing the response with the variable type. This variable is part of my test data, but it's not sent to the agent since we only use it to verify the response.
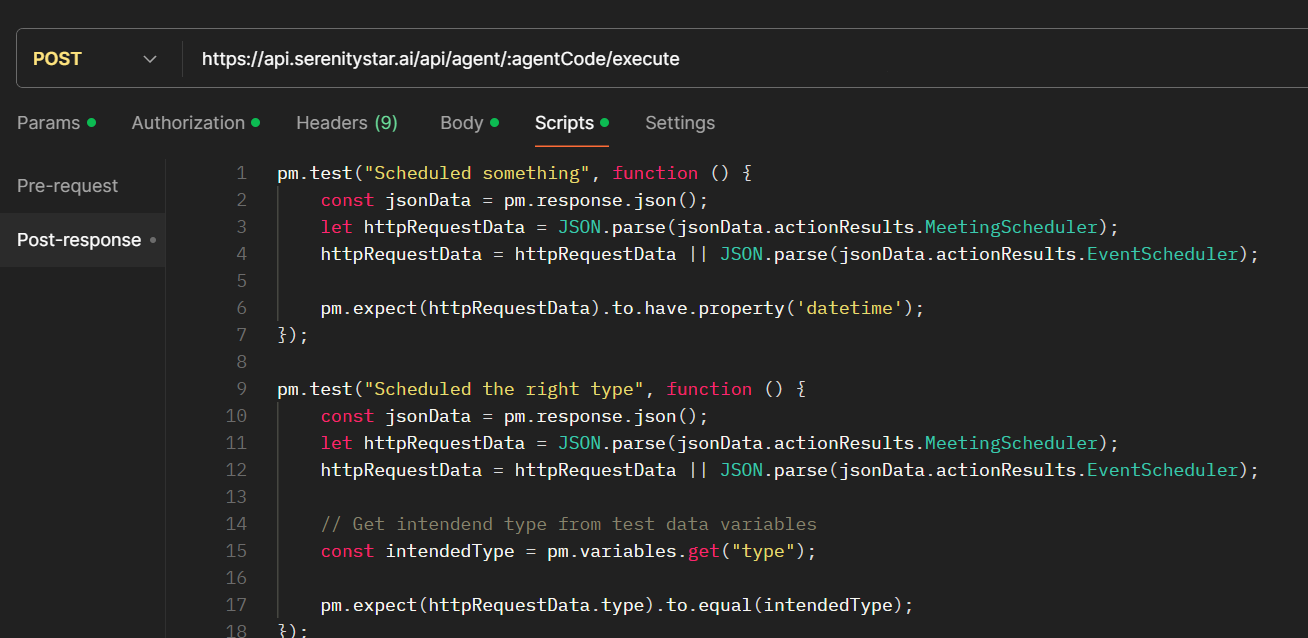
I'll configure a Runner to execute this endpoint using my json file as the data source.
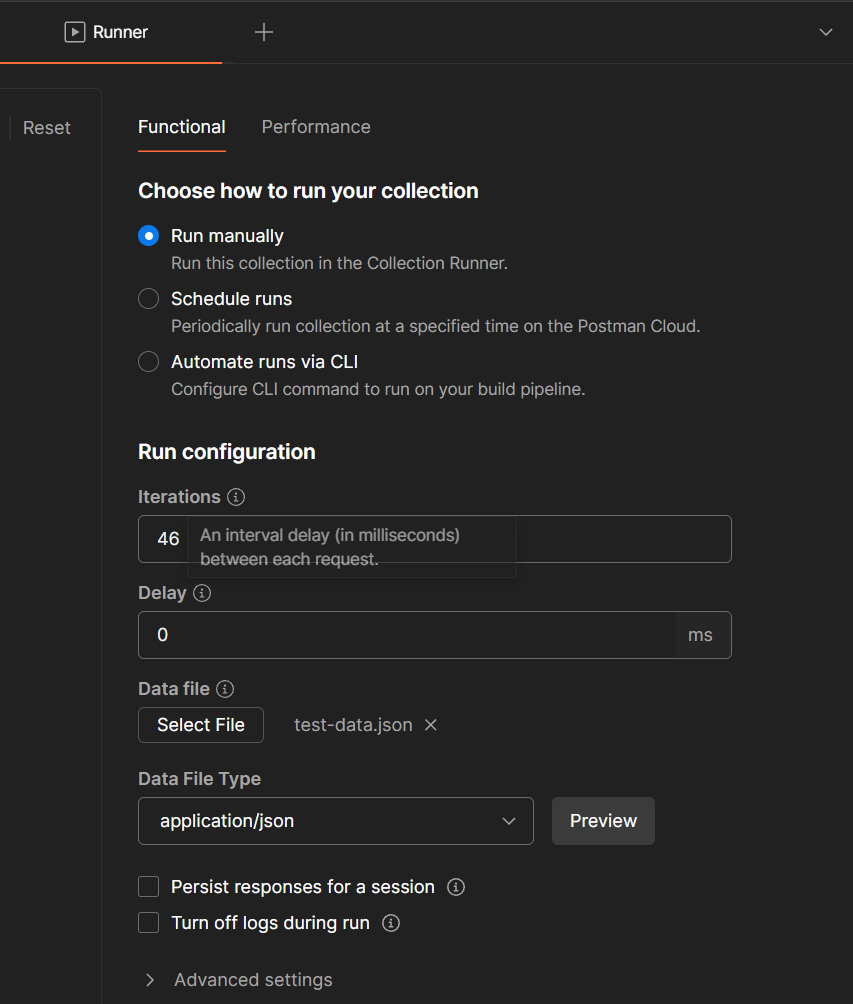
And after running the tests, we can see the results:
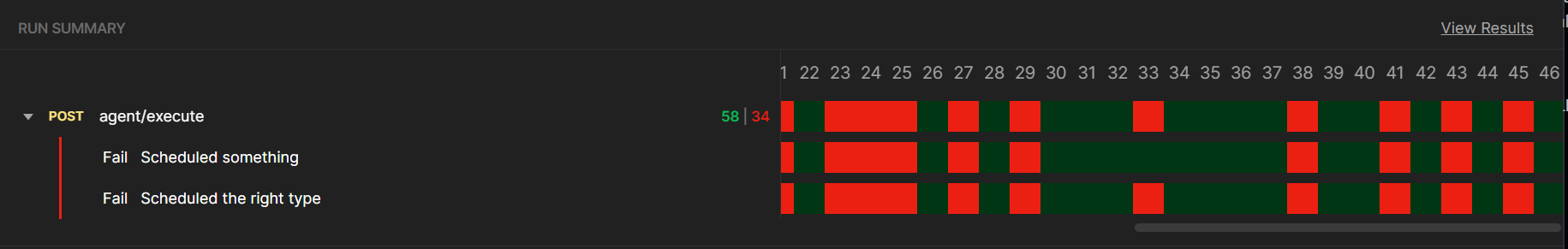
According to the results, sometimes the agent uses the wrong skill, and sometimes, it cannot use any skill at all.
After reviewing the failed tests, I noticed 3 main issues:
- The agent sometimes confuses Meetings with Events, which makes sense since we didn't provide any information on how to differentiate them.
- It has trouble calculating dates with prompts such as "Tomorrow" or "Next Wednesday" unless we provide the current date, time, and day of the week within the prompt.
- It also can't differentiate between optional and required body fields, and it doesn't know details about them, such as the unit of time for the
duration field.
Improving the agent
Issue 1: Differentiating between Meetings and Events
This should be easy to fix. We need to change the skill's description to provide more information.
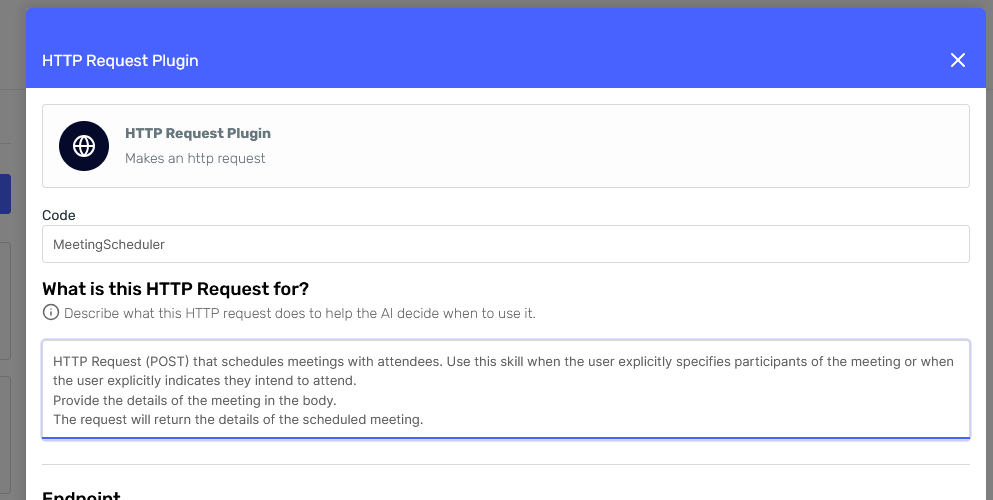
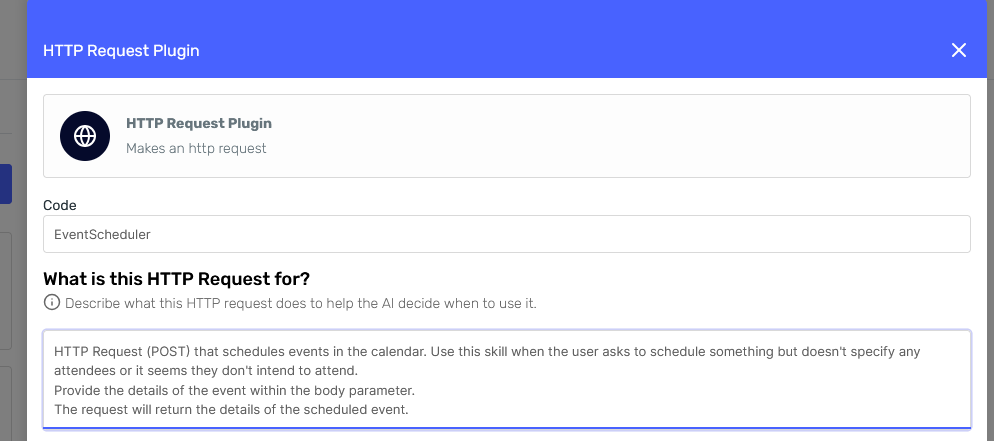
The improvements are:
- Now we're indicating when to use this skill.
- We're specifying the skill is actually an HTTP request, so it's easier for the agent to understand why it needs a body. And we're also stating that a body must be provided to strengthen that point.
- Finally, we're indicating the skill's expected output.
Issue 2: Calculating dates
We could fix this by adding the "TimePlugin," which includes a set of tools to calculate dates and times and returns the current date. But in this case, there's a simpler solution.
We can use Liquid to indicate the current date in the "Ask" field, like so:
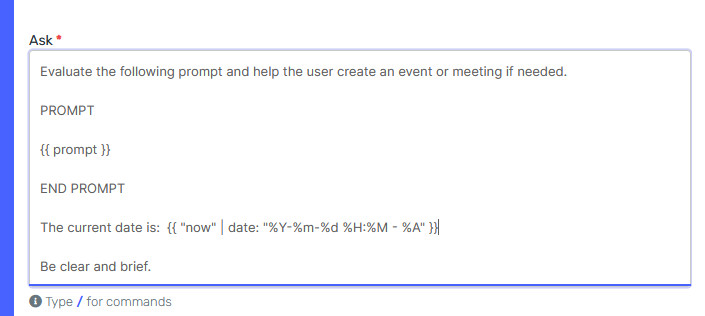
The liquid expression prints the date in the following format "2025-01-15 15:10 - Wednesday". Read more about this here
💡 Including just the minimum required skills is a good idea for performance and to avoid confusing the agent.
Issue 3: Building a valid body
This can be done by improving the body description, like so:
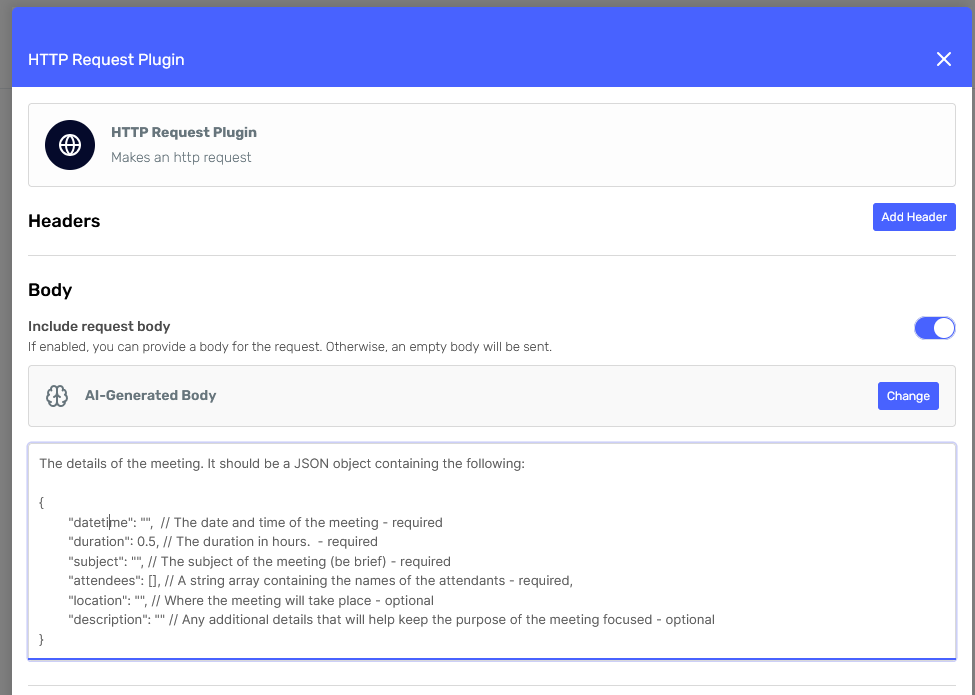
We're now providing a description for each field, indicating when they're required or optional, and details about the data type and units.
Testing the improved agent
We can run the tests again after saving and publishing the agent with these changes.
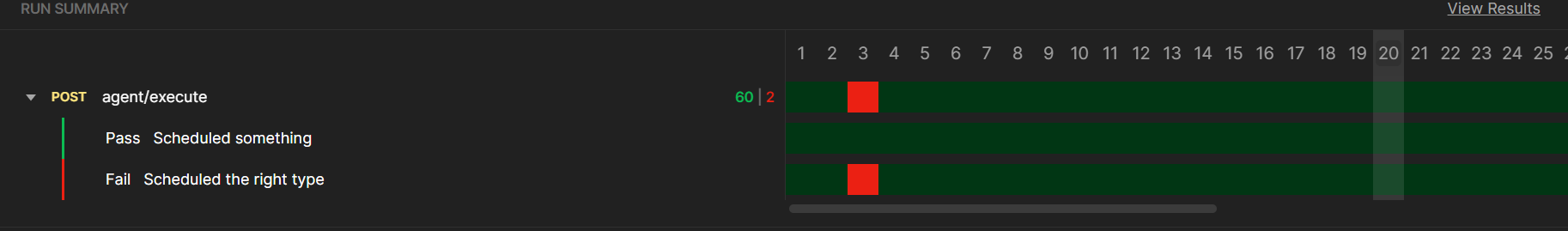
The results look much better now. However, we can keep iterating and testing by following the same process.
Final tips on configuring agents with skills
To sum up, here are some tips to get the best results while configuring an agent with skills:
Choose a clear representative Code for your skill: This, along with the description, will help the agent determine when to use it and will also help you find it in the agent's response and logs.
- Write detailed descriptions: The Skill description is key to instructing the agent when and how to use it. Write anything you think is relevant, including constraints, what the endpoint will return, and when not to use it.
- Describe the body (or any other skill parameters) thoroughly: If the agent needs to create a body for your request, make sure it knows the details of each field, such as data types, which are required and which are optional, types of units, etc.
- Include the minimum skills needed to do the job: This will help the agent avoid confusion and improve performance. If you think your agent is overloaded with skills, you may want to replace some with Liquid or use the Agent executor skill to call specialized agents for each task.
- Try different models: If the model you selected for your agent is not performing as expected, try a different one. Read the documentation on each model to see which one may perform better for your use case.
- Test thoroughly: Make sure the agent performs well on different cases. Users may provide diverse prompts, and we don't want to overfit the agent to a specific type of input.
- Iterate: Keep iterating. We can always return to a previous version of the agent, so don't be afraid to make changes and test them.