Identity Verification in Conversational Agents - Context & Flow Control
One of the most powerful features when designing LLM-driven conversational agents with connected tools is their ability to handle persistent context and multi-step validation flows. In this article, we explore how we implemented an identity verification flow within a customer support agent for online order management, leveraging conversation context, dynamic prompting, and agent skills.
🔧 The Use Case
The agent is defined as a Customer Support Agent for online orders, structured into three main stages:
-
Agent introduction. The agent greets the user, introduces itself, and explains what it can help with.
-
Identity verification.
- Sends a 6-digit verification code using an API (
SendVerificationCode). - Saves the
MessageIdreturned by the API as a conversation variable. - Once the user enters the code, it executes a second skill (
ValidateVerificationCode) using that sameMessageIdand the verification code provided.
- Sends a 6-digit verification code using an API (
-
Open conversation. After validation, the agent unlocks the rest of the prompt, allowing free-form interactions such as checking orders, reporting issues, or submitting claims.
🧩 Conversation Context Structure
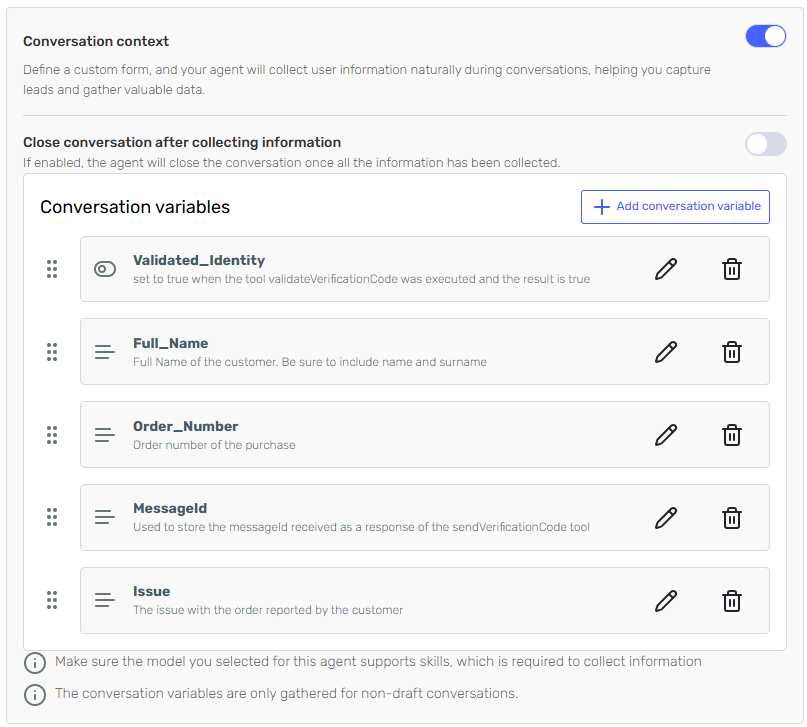
The conversation context includes a set of variables used to maintain state across the chat and control the logic flow:
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Validated_Identity | boolean | Indicates if the user has completed identity verification. |
MessageId | string | ID returned by the SendVerificationCode API. |
Full_Name | string | Full name provided by the user. |
Order_Number | string | The user’s order number. |
Issue | string | Description of the issue reported. |
Each of these variables is updated dynamically based on the outcome of each skill.
For instance, when ValidateVerificationCode runs successfully, it sets Validated_Identity = true, which dynamically expands the prompt to the next section.
Need step-by-step setup instructions? See the Conversation Context docs: Conversation Context documentation
⚙️ Step-by-Step Execution
1. Sending the Verification Code
The flow begins with SendVerificationCode, which receives the user’s Order_Number and returns a MessageId. The details of this execution can be seen in the skill execution details:
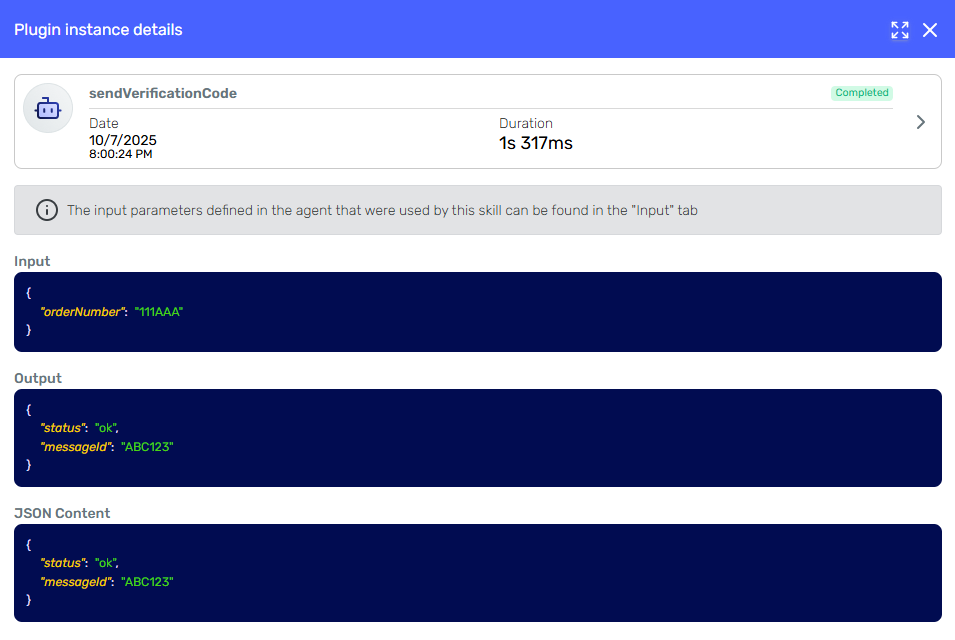
The MessageId obtained is stored automatically in the conversation and referred in the prompt. This way, the agent can reference it later without exposing it to the user.
2. Validating the Code
When the user enters the received code (e.g., “123456”), the agent executes ValidateVerificationCode with:
{
"MessageId": "ABC123",
"verificationCode": "123456"
}
If the API returns success (true), the system sets:
{
"Validated_Identity": true
}
The prompt then expands dynamically, unlocking the next part of the agent’s capabilities. This is achieved using Dynamic Prompting with Liquid templating. The agent's core instructions are wrapped in a conditional block that checks the value of our conversation variable:
{% if conversationVariables.Validated_Identity == "true" %}
... rest of the prompt with full capabilities ...
{% endif %}
This ensures that the agent only gains access to its full set of instructions (e.g., checking orders or reporting issues) after the Validated_Identity variable is set to true. Before validation, it is restricted to only the identity verification flow, making the process secure and controlled.
3. Final Context and Stored Data
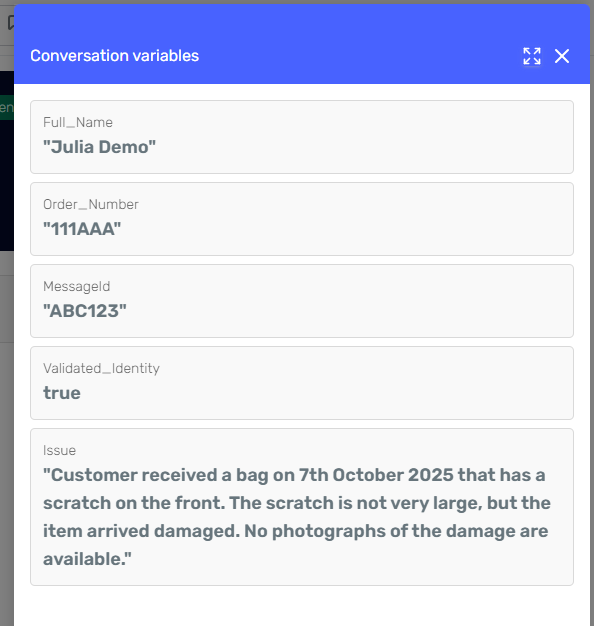
At the end of the flow, the agent has collected and stored all relevant data in its context:
{
"MessageId": "ABC123",
"Full_Name": "Julia Demo",
"Order_Number": "111AAA",
"Validated_Identity": true,
"Issue": "Customer received a bag on 7th October 2025 that has a scratch on the front. The scratch is not very large, but the item arrived damaged. No photographs of the damage are available."
}
This data remains available throughout the conversation lifecycle, enabling subsequent actions — such as creating a support ticket, checking order status, or escalating the case to a human agent.
🧠 Technical Insight
This example demonstrates how an LLM-based agent can manage stateful, conditional conversations while maintaining natural flow. By combining LLM reasoning with structured conversation context, the agent can:
- Keep coherence across multiple steps.
- Reuse results from previous skill executions.
- Dynamically control prompt visibility based on context variables.
This hybrid approach allows the agent to understand natural language while also operating within a deterministic, context-driven logic layer — creating secure, reliable automation.
✨ Conclusion
This verification workflow highlights how intelligent conversational agents can go beyond text responses — integrating identity validation, process automation, and secure logic control, all through natural conversation. The key lies in persistent context and logical orchestration across skills, forming the backbone of robust conversational experiences.
For more details on configuring Conversation Variables and Conversation Context in your agent, see the specific documentation.
Want to have this exact use case in your tenant?
- Sign up or sign in to your Serenity account.
- Click the link below to import the agent and copy this identity verification flow directly into your tenant:
👉 Import the agent: Import Verification Flow (Copy to my tenant)
After importing, you can customize conversation variables, skills, and API integrations to match your processes.
